D.27 Answers: Tests for paired means
Answers to exercises in Sect. 29.11.
Answer to Exercise 29.1:
: and : :
differences are positive when the dip rating is better than the raw rating.
; larger than 0.05:
the evidence doesn’t support the alternative hypothesis.
Answer to Exercise 29.2:
1. Because it is the bloood pressure reduction,
and a reduction is what the drug is meant to produce,
so expect the reductions to be positive nunmbers.
2. Differences shown below.
3. Histogram of differences: Fig. D.7.
4. : and : (because the differences are reductions).
5. .
6. (one-tailed test).
7. Very strong evidence () that the drug reduces
the average systolic blood pressure (mean reduction: 8.6 mm Hg) in the population.
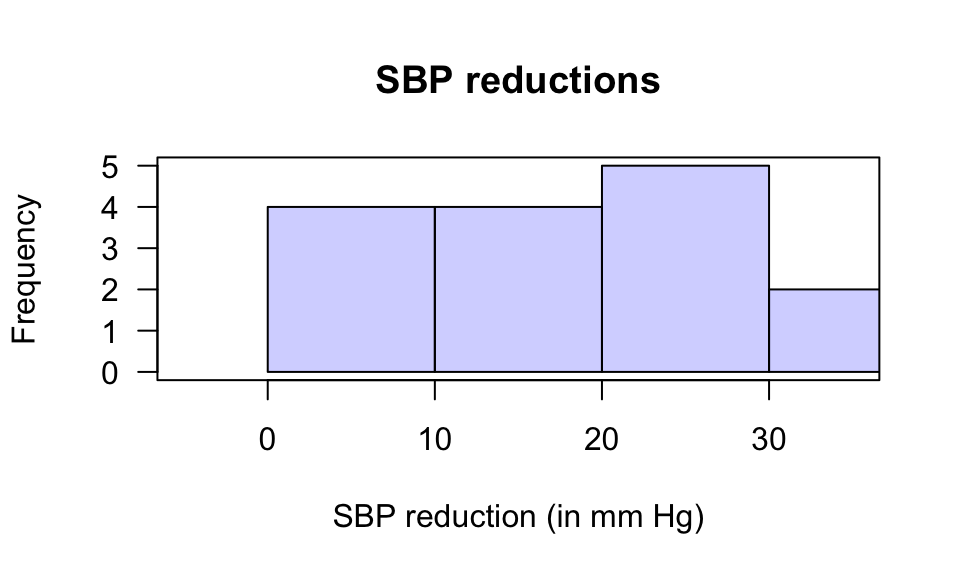
FIGURE D.7: A histogram of the systolic blood pressure reductions (in mm Hg)
Answer to Exercise 29.3:
: and : ,
where differences are positive when the intention to smoke is reduced after exercise.
; -value larger than 0.05:
the evidence doesn’t support the alternative hypothesis.
No evidence () that the mean ‘intention to smoke’ reduced after exercise in women
(mean change in intention to smoke: -0.66; std. error: 0.37).
Answer to Exercise 29.4:
: and : ,
where differences refer to the reduction in ferritin.
and and ,
so .
is ‘small’; (actually ):
the evidence doesn’t support the alternative hypothesis.
Since , the test may not be statistically valid
(the histogram of data (Fig. D.8)
suggests that the population might have a normal distribution),
though the -value is very large so it probably makes little difference.
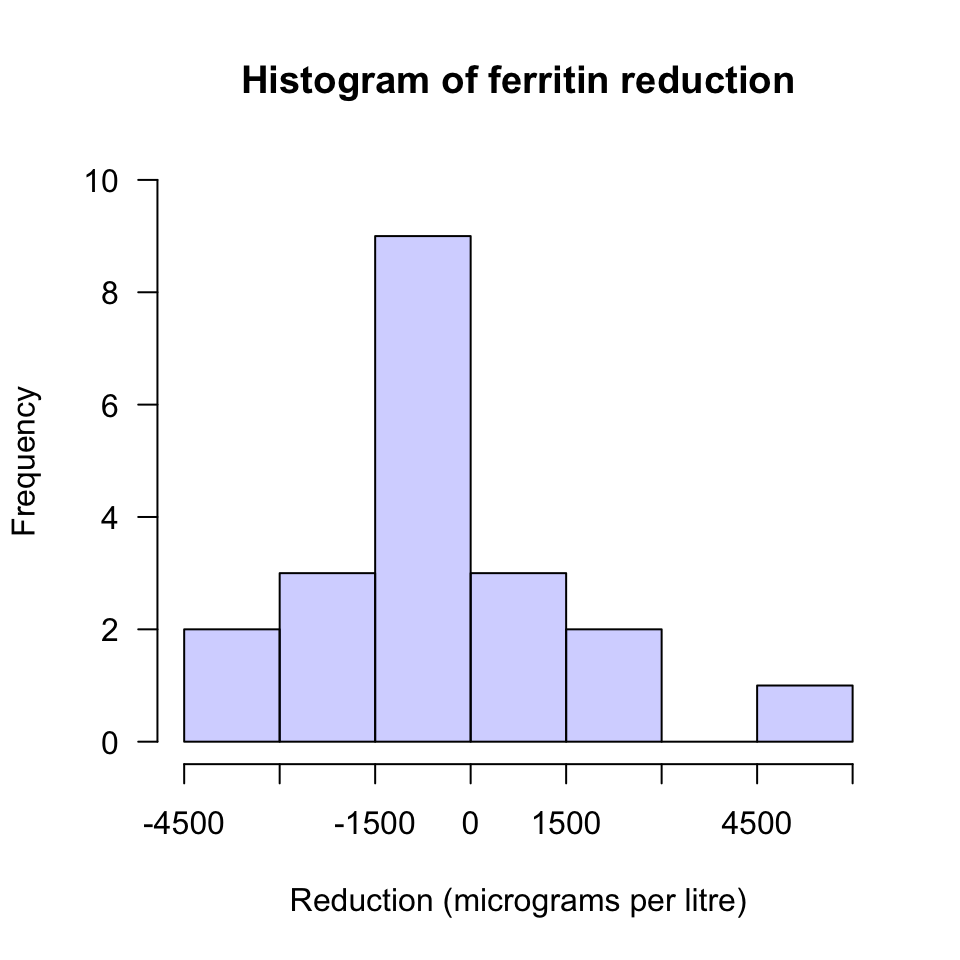
FIGURE D.8: A histogram of the change in ferritin concentration