12.13 Exercises
Selected answers are available in Sect. D.12.
Exercise 12.1 A study (Henderson and Velleman 1981) recorded the number of cylinders in many models of cars (Table 12.7). The number of cylinders is quantitative discrete, but with so few different values, this variable could be plotted with some of the graphs used for graphing qualitative data.
For these data:
- Produce a dot chart.
- Produce a histogram.
- Produce a bar chart.
- Produce a pie chart.
| Number of cylinders | Number of cars |
|---|---|
| 4 | 11 |
| 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 14 |
Exercise 12.2 A study of lime trees (Tilia cordata) recorded these variables for 385 lime trees in Russia (Schepaschenko et al. 2017; Dunn and Smyth 2018):
- the foliage biomass, in kg;
- the tree diameter (in cm);
- the age of the tree (in years); and
- the origin of the tree (one of Coppice, Natural, or Planted).
Exercise 12.4 A study of fertilizer use (Lane 2002; Dunn and Smyth 2018) recorded the soil nitrogen after applying different fertilizer doses. These variables were recorded:
- the fertilizer dose, in kilograms of nitrogen per hectare;
- the soil nitrogen, in kilograms of nitrogen per hectare; and
- the fertilizer source; one of ‘inorganic’ or ‘organic.’
Exercise 12.5 A survey of voice assistants (e.g. Amazon Echo; Google Home; etc.) conducted by Nielsen asked respondents to indicate how they used their voice assistant; options given were:
- Listening to music;
- Search for real-time info (e.g. traffic; weather);
- Search for factual info (e.g. trivia; history);
- Listen to news;
- Chat with voice assistant for fun;
- Use alarms, timer.
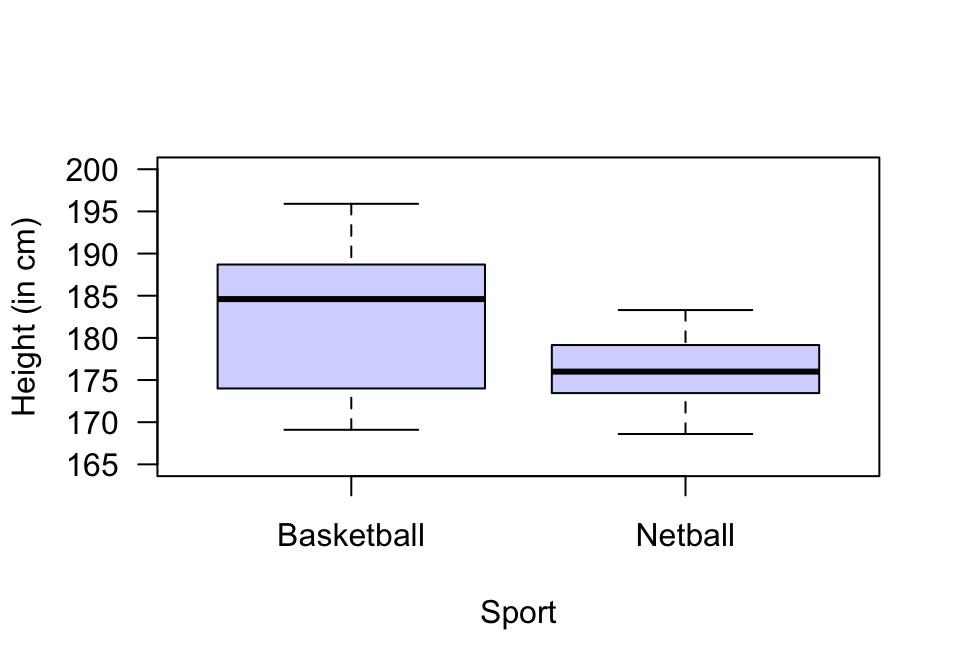
FIGURE 12.40: The heights of female basketball and netball players attending the AIS
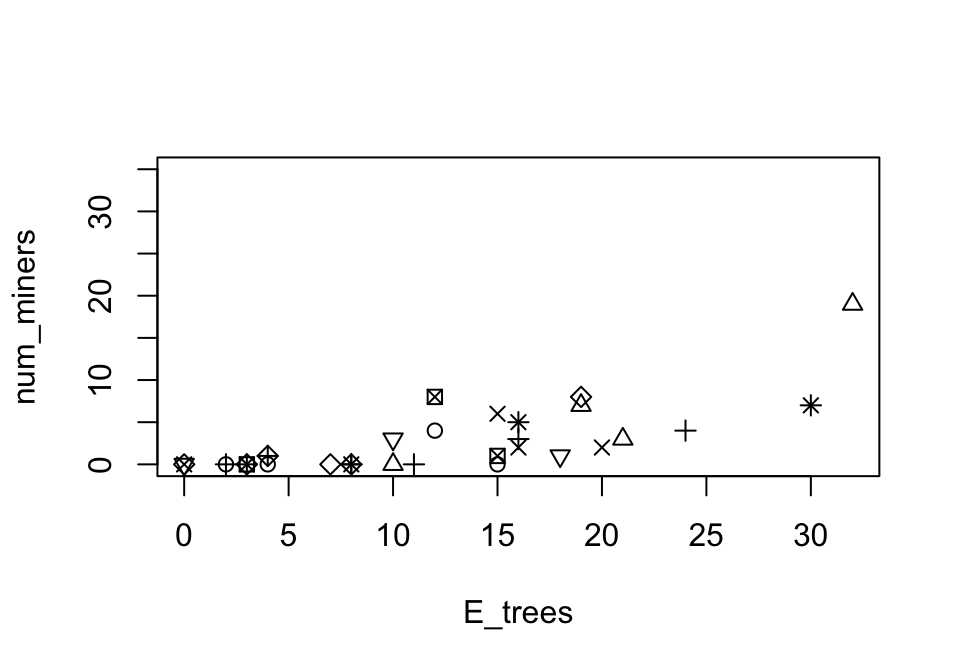
FIGURE 12.41: The number of noisy miners and the number of eucalyptus trees
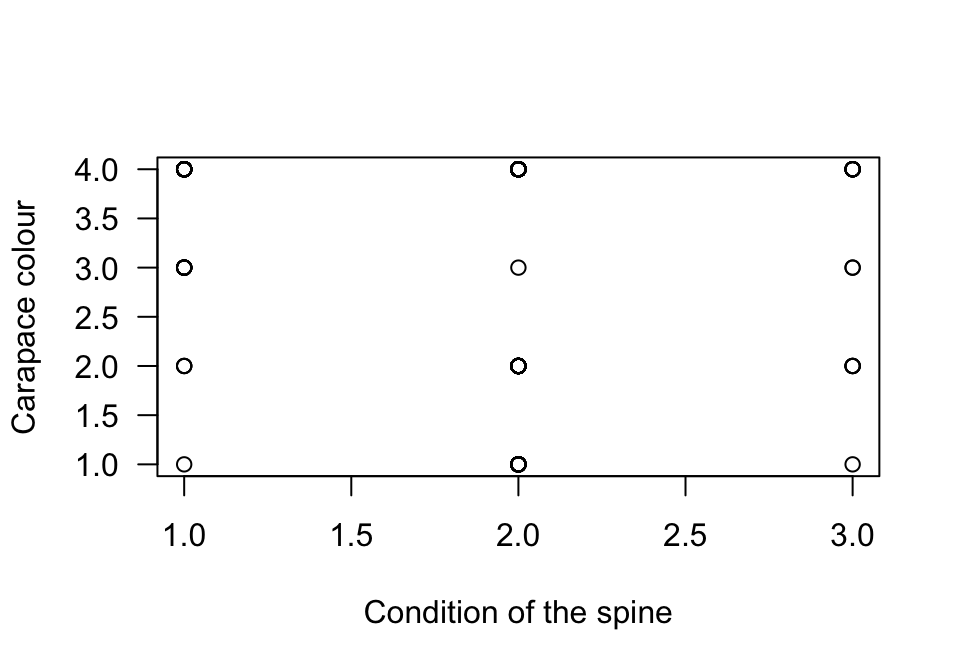
FIGURE 12.42: A scatterplot of the colour of female horseshoe crabs and the condition of their spines. There are no missing values.
Exercise 12.9 A study (Danielsson et al. 2014) examined the change in MADRS (a quantitative scale measuring level of depression) and treatment group (whether each person was treated using: exercise; body awareness; or advice).
- What is the response variable?
- What is the explanatory variable?
- What graphs would be useful for exploring the data and the relationships of interest?
| Office A | Office B | Office C | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | 24.1 | 25.3 | 25.7 |
| Minimum | 16.4 | 15.9 | 20.1 |
| Q1 | 22.8 | 23.8 | 24.6 |
| Median | 24.4 | 25.5 | 26.1 |
| Q3 | 25.5 | 26.9 | 27.2 |
| Maximum | 27.4 | 31.0 | 30.3 |
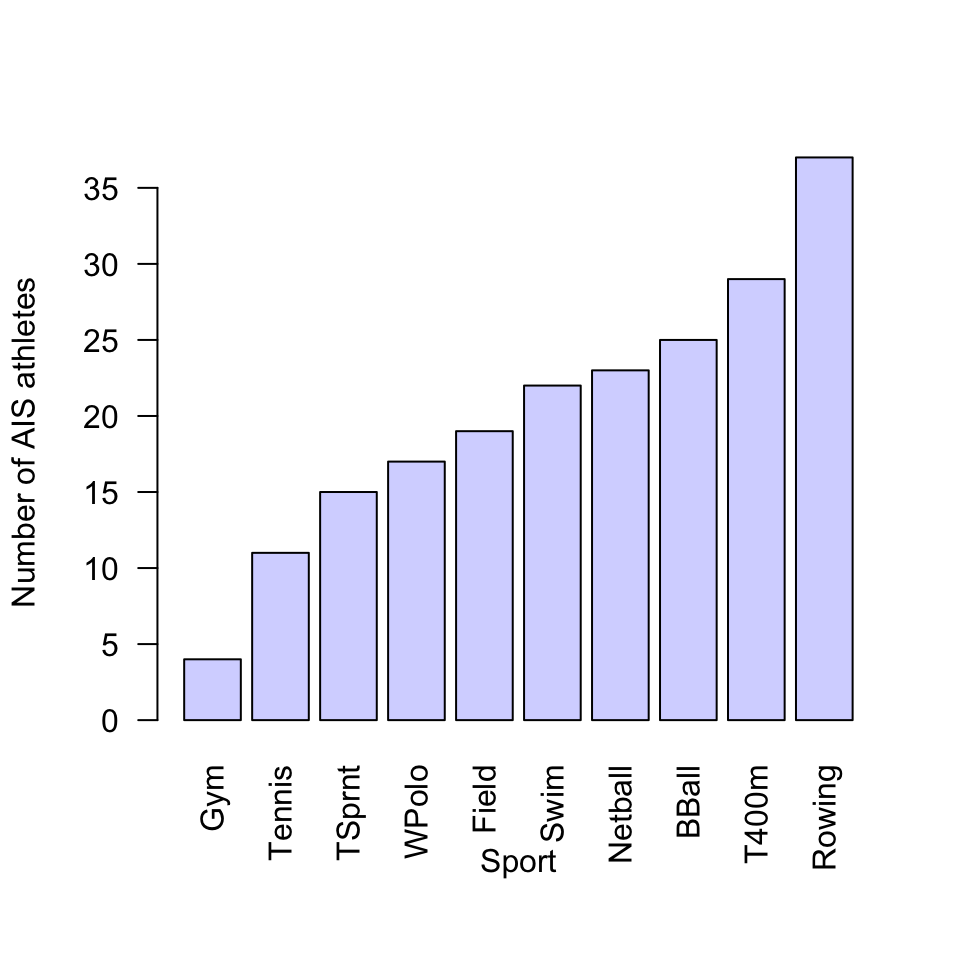
FIGURE 12.43: Sports played by athletes in the AIS study
Netball was derived from basketball: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Netball#History↩︎