6.3 Extraneous variables and variation in the response

Other variables probably exist which are associated with changes in the value of the response variable; these are called extraneous variables.
All extraneous variables are, by definition, related to the response variable. An extraneous variable may or may not be associated with the explanatory variable as well. Extraneous variables may have other names too (Table 6.1), though these names are used inconsistently by researchers (Dunn et al. 2016).
![]()
The problem with confounding is a relationship between the response and explanatory variables may be evident, but only because both of these variables are related to the confounding variable (Fig. 6.2).
Example 6.1 (Confounding variables) A relationship exists between carrying cigarette lighters, and lung cancer: people who carry cigarette lighters are more likely to get lung cancer.
The only reason that this relationship exists is because of a confounding variable: whether or not the person is a smoker. A smoker is more likely to carry a cigarette lighter, and is also more likely to develop lung cancer.Managing confounding is very important, as confounding can completely change the conclusion drawn from the study (see the example in Sect. 14.1) and hence can compromise internal validity. Ways of managing confounding are discussed in Sects. 7.2 and 8.2.
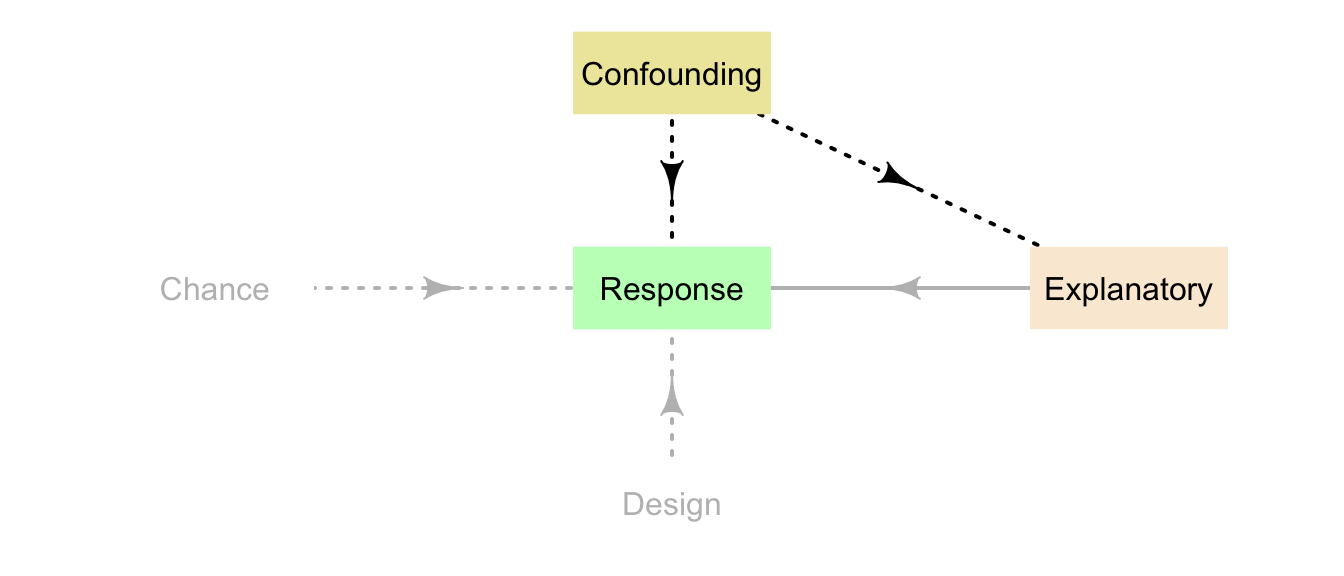
FIGURE 6.2: Confounding variables are extraneous variables associated with the response and explanatory variables
Sometimes confounding variables are not measured, assessed, described or recorded; these confounding variables are then called lurking variables (Fig. 6.3). Failure to acknowledge lurking variables can lead to wrong conclusions (for example, see Sect. 14.1).
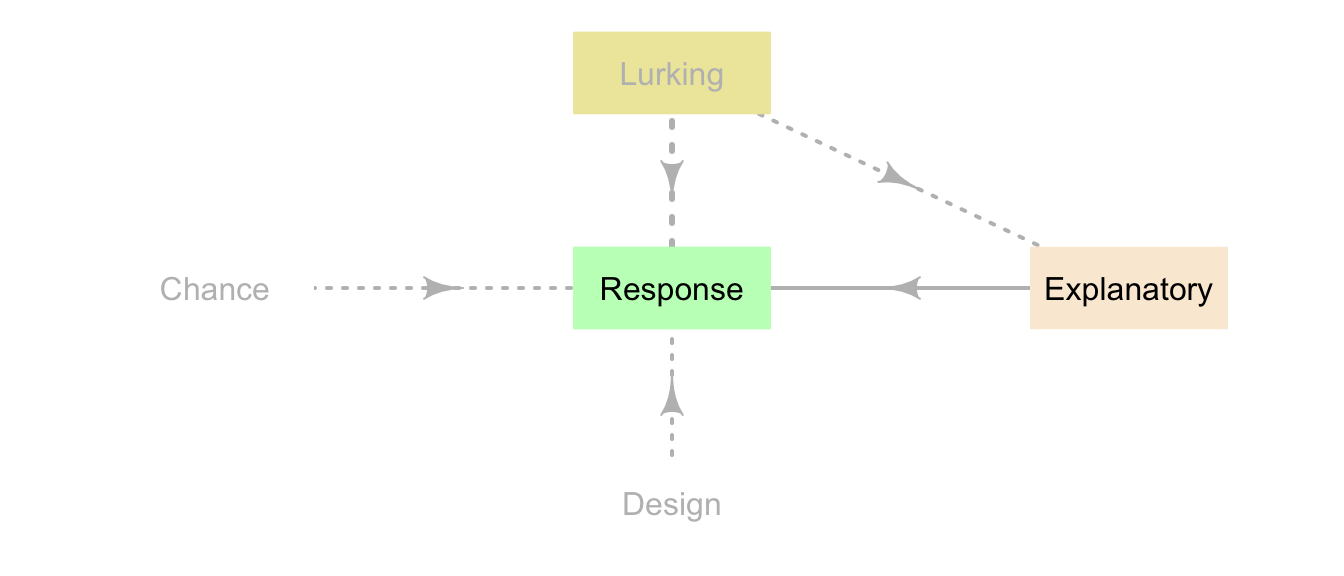
FIGURE 6.3: Lurking variables are associated with the response and explanatory variables, but are not recorded
Example 6.2 (Lurking variables) Consider the relationship between carrying cigarette lighters, and developing lung cancer (Example 6.1), where the confounding variable is ‘whether or not a person is a smoker.’
If the researchers had failed to record whether or not each subject was a smoker, ‘whether or not a person is a smoker’ would be a lurking variable (Fig. 6.4). If they had recorded the smoking status of the subjects during data collection, then the smoking status would be a confounding variable (but not a a lurking variable), and we would have ways to use this information to correctly interpret the results.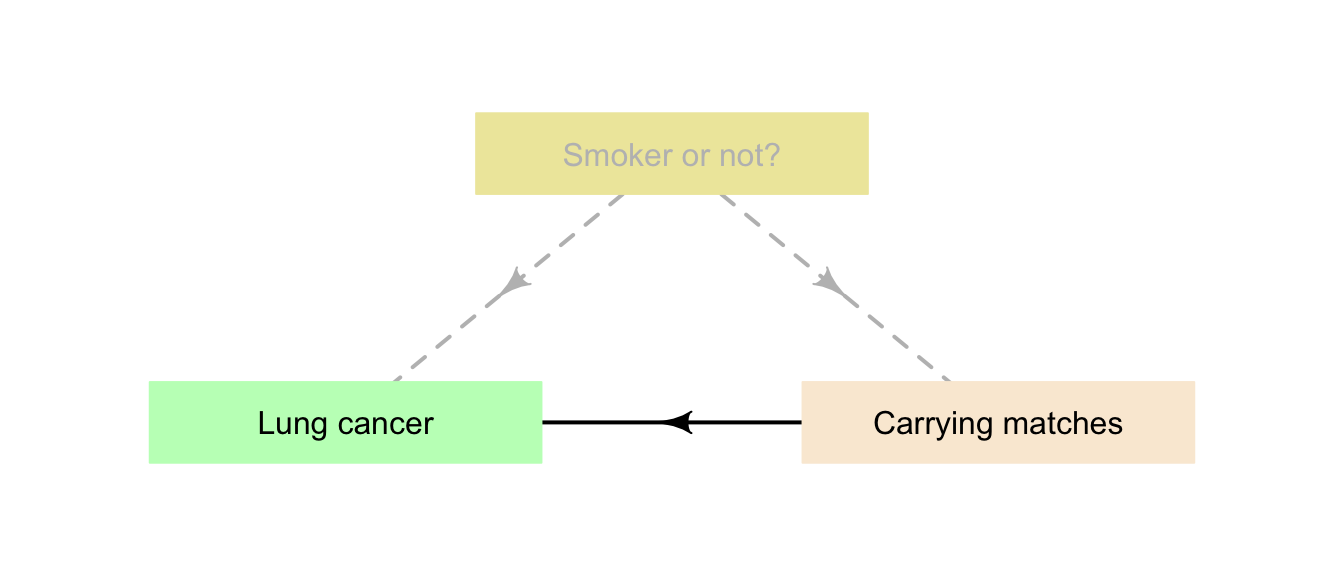
FIGURE 6.4: An example of a lurking variable
To clarify (Table 6.1):
- Extraneous variables are all related to the response variable, by definition.
- Some extraneous variables are also called confounding variables: if they are also related to the explanatory variable.
- Some confounding variables are also called lurking variables: if they are not measured, assessed, described or recorded.
Some unknown extraneous variables will be associated with the response variable only, and so become part of variation due to chance (i.e. unexplained). These terms are not always used consistently by all researchers (Flanagan-Hyde 2005).
| Type | Associated with response | Associated with response and explanatory |
|---|---|---|
| Measured or observed | No special name: extraneous | Confounding (not lurking) |
| Not measured or observed | Becomes part of ‘chance’ | Lurking |
To avoid lurking variables, researcher generally collect lots of information about the individuals in the study (such as age and sex if the study involves people) and circumstances of the study (such as the temperature) that may be relevant, in case they are confounding variables.